Creating an ODBC connection (DSN)
The functions for importing nest information use ODBC connections to read and write from an SQL database. The system currently supports SQL implementations from Microsoft, Sybase and Oracle.
In the text that follows the names 'Settings' and 'Setup' refer to the System Management functions Import/Export > Nesting SQL Database > Connection Settings and Import/Export > Nesting SQL Database > Setup.
In the System Management Application there are a three settings on the 'Settings' panel that are used for the ODBC connection:
- Connection Name (DSN)
- Username
- Password
When these values have been set, the user can create the ODBC connection by starting the 'Setup' function.
The user is then prompted to create a DSN when it not already available and no configuration file for automatic DSN creation is present (see below).
The following figures show how an ODBC connection (DSN) is created.
The DSN can be either a 'User DSN' or a 'System DSN'. If you have the appropriate rights, choose 'System DSN'.
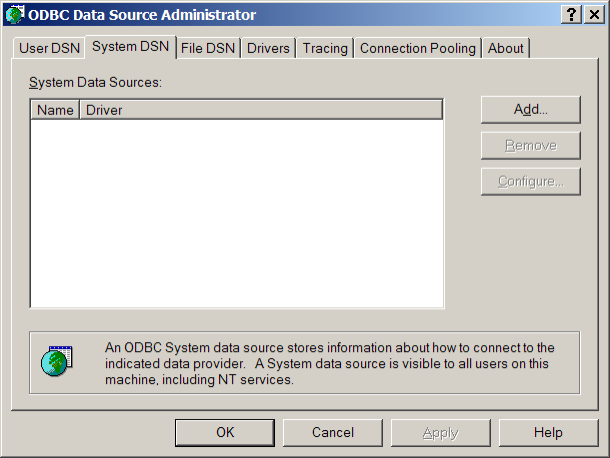
Click 'Add...' to create a new DSN.
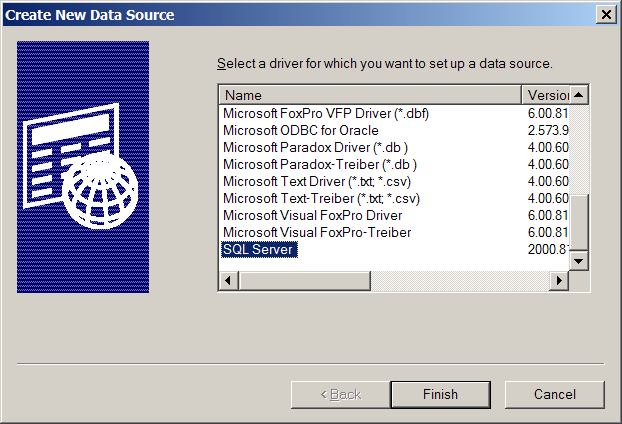
Select the desired SQL driver, in this case Microsoft SQL Server.
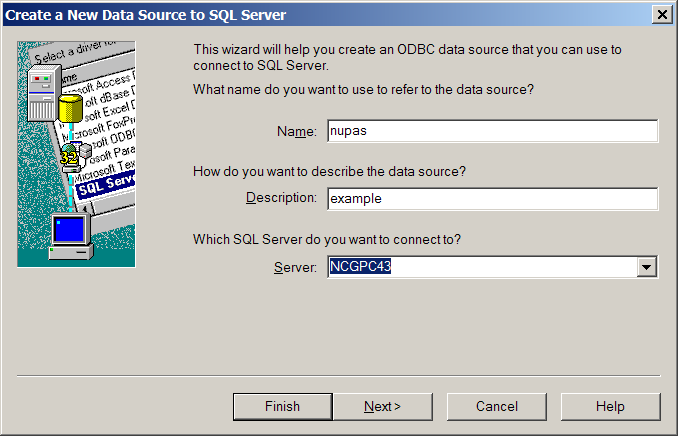
This is where the value specified by 'Connection name (DSN)' on the 'Settings' panel must be typed ('nupas' in this case).
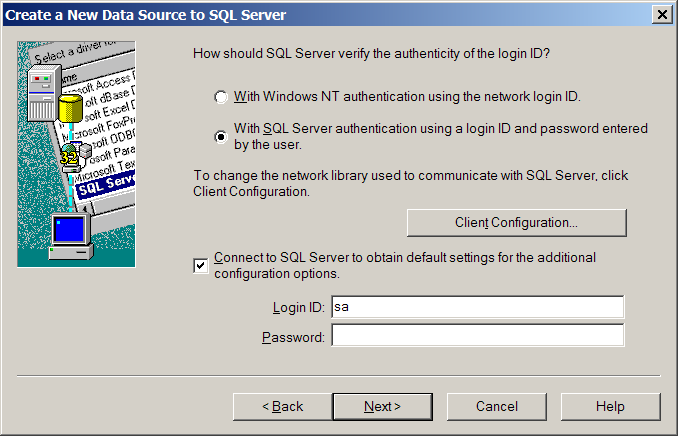
Choose SQL Server authentication and type the 'Login ID' and the 'Password' (the 'Username' and 'Password' from the 'Settings' panel.
The rest of the panels maintain their default settings.
The connection can be tested:
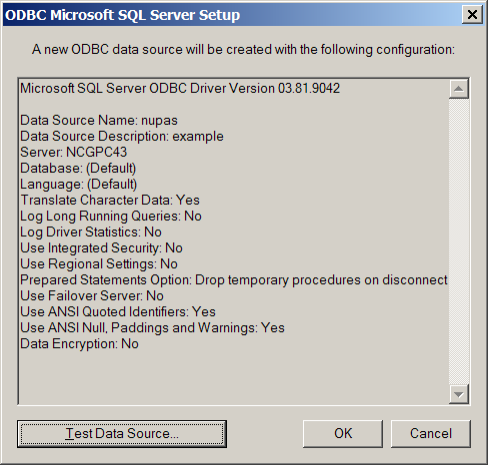
The information about the created DSN is written to %ncghelps%\odcb\nupas.dsn.cfg
Where 'nupas' is the DSN name. Other machines will use this file to create the same DSN automatically. If you want to change the DSN, delete this file and run the 'Setup' function again.