Special case: multiple intersections with plate and fixed value relations
There is a special situation of a face plate on plate where the order of defining the face plate relations is important:
-
The first relation is a fixed value relation.
-
The second relation is to a plate.
-
The third relation is a fixed value relation.
-
The second relation (the plate) has two or more intersection points with the both the first and the third relation.
In such a case the face plate relations must be defined following the plate contour's direction. In the side and the frame view this is counter-clockwise, and in the top view it is clockwise. The indication point of the second relation (the plate) must be on that side of the plate where the face plate is to be positioned.
Example 1: frame view
The image below illustrates the case in frame view.
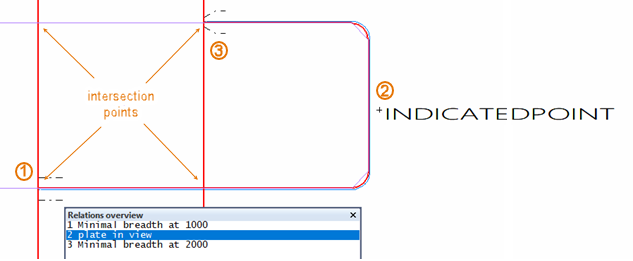
The relations (1, 2, 3) have been defined in counter-clockwise order, and the straboard side of the plate has been indicated when defining the second relation (the plate). The second relation has two intersection points with both the first and the third relation, which are fixed value relations.
Example 2: top view
The image below illustrates the case in top view.
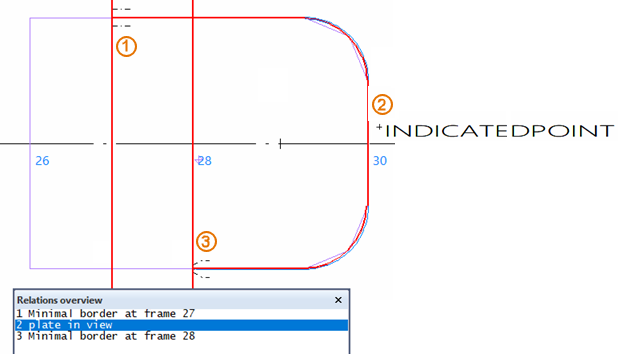
The relations (1, 2, 3) have been defined in clockwise order, and the fore side of the plate has been indicated when defining the second relation (the plate). The second relation has two intersection points with both the first and the third relation, which are fixed value relations.