Cable route air jumps
Normally, cables are routed via the cable way objects defined in the 3D model. In specific situations, the cable route can also travel through air, which is called an "air jump". The cable router can use an air jump to establish a better route for a cable, unless the given conditions prevent the jump.
Air jump terminology
Air jump is a part of a cable route that does not use a cable way host object but is modeled as a segment. This can be, for example, a segment that jumps from one cable tray to another.
Head/tail jump is the part of the cable route that connects the head equipment to the first node, or the last node to the tail equipment. These jumps are never modeled as segments.
Double air jump means that there are two or more consecutive air jumps. These are not allowed in cable routes.
Branch node is a node where one or more branch runs connect to the main run. If several branches are close to each other, the cable routing network creation inserts a single branch node for them, at an average location. If the branch node would be too close to the end node of the main run, the branch node is not created, but the branch runs are connected directly to the end node instead.
Combined node refers to two or more network nodes located at the same spot. This typically occurs when the ends of cable way runs collide or overlap. To prevent this during the 3D modeling phase, ensure there is sufficient empty space between separate runs and use actual branch cable tray parts to model the branch locations. Additionally, you can set Tolerances that enable the cable routing network creation to replace end nodes and combined nodes within the given tolerance with a single node.
Allowed air jumps
Air jumps are allowed in the following situations.
-
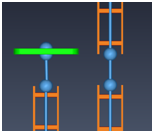
Cables can jump directly from the head equipment to the tail equipment, without using cable trays, if both pieces of equipment are in the same 3D space and their distance is less than the maximum distance defined in the cable router settings in Cables.
-
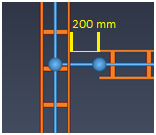
Cables can jump to a cable penetration or another cable tray, if the 3D jump distance does not exceed 500 mm, depending on the orientation of the parts.
-
Cables can jump to a cable tray that is perpendicular or angled to the cable penetration or cable tray branch, if the 3D jump distance does not exceed 500 mm, depending on the orientation of the parts.
-
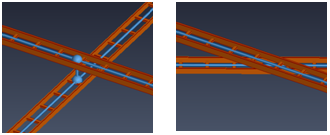
Cables can jump vertically between the center lines of two cable trays, if the angle between trays is at least 45° and the 3D jump distance does not exceed 500 mm, depending on the orientation of the parts.
-
Cables can jump to T-pieces, cross pieces, and curves.
Disallowed air jumps
Air jumps are not allowed in the following situations.
-
Cables cannot do an air jump if another model object is blocking the straight line between the nodes. Note that the space around the straight line is not checked for collisions.
Tip: You can exclude objects from this check, as described in Network.
-
Cables cannot do a double air jump, such as a jump from the head equipment to the end of a cable tray and then onward to the first node of a penetration.