Define the main user and create databases
Define the main user and create databases in Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio.
You will need to define the db_owner user role for the main user. This role will allow the main user to create database tables and update the database structure when upgrading to a new version. For more information on the roles, see User roles.
You will need to create three types of databases: a management database, a project database and shared databases.
-
The management database includes a list of different project databases, shared databases, and users.
-
The project database contains all the CADMATIC Electrical project data in the SQL Server instance.
-
The shared databases contain shared design content, such as cable types, product information, and plate definitions.
You can name these databases any way you want. In these instructions, the databases are named EDBManagement, EDBProject and EDBUserCommon.
Do the following:
-
Connect to the SQL Server database.
-
Add a new user (who you will define as the main user later):
-
In Object Explorer, open Security > Logins. This folder contains all SQL Server users and user groups.
-
Right-click Logins, and select New Login.
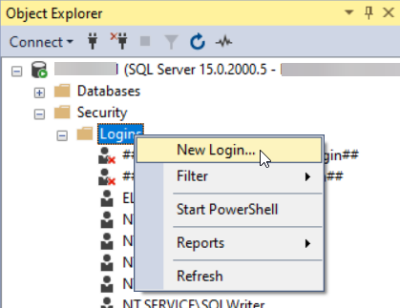
The Login - New dialog opens.
-
For Login name, enter the username in the format [domain name]\[Windows username].
-
Click OK. The program creates the new user into the user folder.
-
-
Create the databases:
-
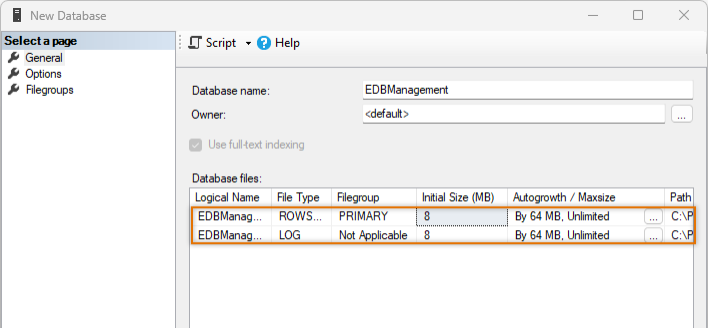
In Object Explorer, right-click Databases and select New Database. The New Database dialog opens.
-
In the Database Name field, enter the desired name. In this example, EDBManagement is used.
The program creates two files: a ROWS file that contains the actual database data, and a LOG file that contains the SQL commands that are sent to the database.
-
Define the default sizes:
-
For the ROWS file, for Initial Size, enter 64 as the value.
-
For the LOG file, enter 32 as the default size.
-
-
Define the growth rates:
-
For the ROWS file, in the Autogrowth / Maxsize column, click the
 button. The Change Autogrowth for [file name] opens.
button. The Change Autogrowth for [file name] opens. -
For In Megabytes, enter 32 as the value.
-
Click OK.
-
Enter 16 as the growth rate for the LOG file as described.

-
-
Check the default file location in the Path column. You do not need to change the location at this point, but note that the program does not create backups of the files, so you have to do that yourself.
-
Click OK.
-
Create two more databases (in this example named EDBProject and EDBUserCommon) as described, with the following definitions:
Database type
Type
Default size
Growth rate
Project
ROWS
512
256 LOG
128 64 Shared
ROWS
128 64 LOG
64 32
-
-
Define the main user for the databases:
-
Open Security > Logins.
-
Right-click the user name you added in step 1, and select Properties. The Login Properties - [User name] dialog opens.
-
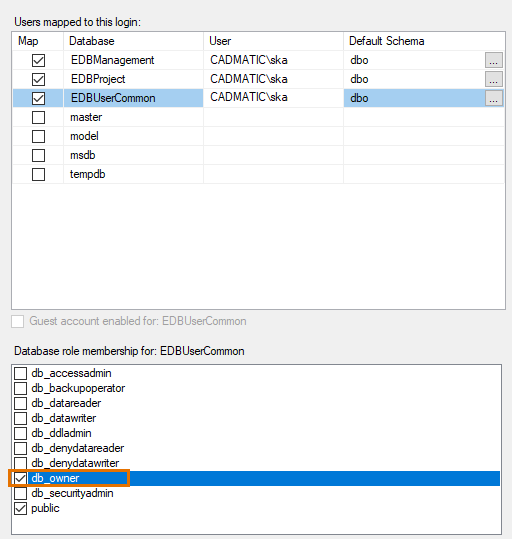
On the left side of the dialog, select User Mapping.
-
On the Map column, select the databases you just created.
-
For Default Schema, enter dbo as the value for each database.
-
One by one, on the list at the bottom of the dialog, select db_owner for each database.
-
Click OK. The program adds the user as the main user for the databases. If you want to check that everything is in order, select Databases > [Database] > Security > Users. The user is visible in the user list.
-
Next, take SQL Server project management into use.