Requirements
The following items are required for the NAPA Steel Integration function to work:
-
A license for the Hull NAPA Steel Interface module
-
A license for the NAPA API. The NAPA Steel Integration function uses the NapaObjectModel API version 2021.2. This API version uses the CodeMeter licensing system, which requires that the CodeMeter User runtime application, available from WIBU Systems, is installed.
- A NAPA system database
- A NAPA user database
Note: NAPA Steel software must be installed on the same computer as CADMATIC Hull, not as a shared drive path.
Integration Settings
Before you can use the Tools > NAPA Steel Integration function, available in the 3D-Contek application, you must define the following settings in the System Management application, Projects > Napa Steel > Integration Settings.
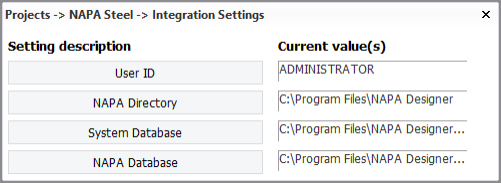
- User ID – User name for NAPA Steel.
- NAPA Directory – Installation directory of NAPA Steel software.
- System Database – Location and name of the system database file (sysdb.db) for NAPA. The file is located in the \bin\Resources folder of NAPA software installation. NAPA installation data is stored in this file.
- NAPA Database – Location and name of the NAPA user database file (napadb.db). The file is located in the \database folder of NAPA software installation. This database contains the NAPA data objects that are accessed by users.
Tip: You can use the Opening Parameters overview in the Help > About NAPA Designer function in the NAPA Designer program to get the required integration settings values.
In addition to the integration settings, you must map the NAPA Steel structural entities like profile types, holes, brackets, stiffener end types, and so on, to CADMATIC Hull structural entities. You do this by defining the NAPA Steel Connection Settings in System Management > Projects > NAPA Steel > Connection Settings. These settings are stored in the files contained in the napa_steel subdirectory of the project's norms directory %NCGNORMS%. The settings can be changed also by manually editing the files. See Settings in the norms for more information.