Set coordinates (C)
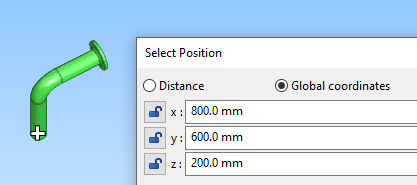
The Set coordinates (C) command opens the Select Position dialog in Global coordinates mode. The values (x, y, z) show the coordinates of the currently active point.
If you are performing a function where the cursor is locked to a plane, you can click Local plane coordinates to see the local (u, v) coordinates instead.
You can do the following:
-
You can check what the current coordinates of the cursor are.
-
You can copy the coordinate values to the clipboard or to another application.
-
You can type the coordinate values or use arithmetic operations to define the new position. Also symbolic names defined as Aliases or Coordinate references can be used here.
-
You can click the lock icon of a distance value or global coordinate so that the value is fixed and does not accidentally change after you close the dialog.

OK applies the coordinate values and fixes the cursor so that it does not move even though you move the mouse.
Cancel closes the dialog without moving the cursor or fixing its position.
Example
In this example, a previously routed pipe starts from coordinates 800, 600, 200 and we want to create another pipe that starts from 1300, 300, 200.
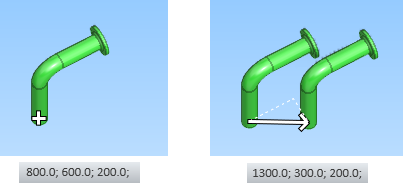
Do the following:
-
Select Piping > Route > Route pipe.
-
Use Move to nearest geometry point (W) to snap to the start of the previously routed pipe.
-
Use Set coordinates (C) to open the Select Position dialog. You can see the current coordinates.
-
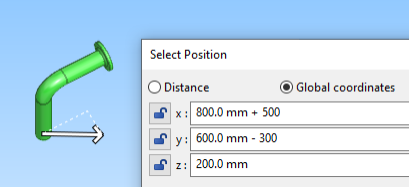
Enter the coordinates for the new pipe as follows:
-
x = 800 + 500
-
y = 600 - 300
-
-
Click OK. The cursor is now fixed to the specified position.
-
Press Space to start routing the new pipe.