Glossary
When a designer is performing routing and selects to add a component, the system performs specification lookup to find out what is the catalog part and catalog size to be inserted. If functional codes used in the specification are configured to use additional lookup dimensions, a single functional code – key size combination can map to multiple variations of the same catalog part. As a result, when adding for example an actuator valve, the system can prompt the designer to choose one of four possible mounting positions. See Functional codes.
The Auto-Trim to Nearest Plane function of Plant Modeller allows the system to automatically shorten or extend the user-specified end of a straight pipe or beam to a plane (planar face) that is found near the end of the object to be trimmed. The user can specify the maximum search distance.
See Trim and Stretch on how to auto-trim pipes and Trim and Stretch on how to auto-trim beams.
Bill of Material. See Define the Bill of Materials.
A line passing through the center of something and dividing it into two equal parts. In CADMATIC Plant Modeller you can for example see the centerline of pipes, snap to them, and use them as reference lines in navigation.
An imaginary line passing through the center of a vessel from the stern to the bow. When facing forward, the center line divides the vessel into port side (PS) on the left and starboard (SB) on the right.
(P&ID) Table which contains information for the automatic filling of database cards.
Center of Gravity. The center of gravity (center of mass) of an object can be defined in the object attributes COG x, COG y, and COG z. The center of gravity is visualized for example in the preview image of the object in the object browser, as described in Object preview.
The Content Categories feature enables you to control which COS user profiles can access model objects, documents, and work requests in a given category. Within this mechanism, users with access to certain categories cannot view data in other categories, while data outside these restrictions remains available to all users. This feature can help protect sensitive data, for example, by preventing subcontractors from seeing each other's designs in a shared model area. See Content Categories.
The DEXPI website at https://dexpi.org defines the objective of the DEXPI initiative to be "to develop and promote a general data exchange standard for the process industry", with a special focus in "the exchange of Piping and Instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs)". Accordingly, to enable this data exchange, the DEXPI initiative has defined an open XML format. Exchanging P&ID related data in the DEXPI format can be useful especially when different design disciplines use different software products, and the distribution and updating of data needs to be managed efficiently.
CADMATIC P&ID can import DEXPI XML files that have been exported from any software that supports DEXPI XML export, and CADMATIC P&ID can also export this format. Imported attribute data can be stored in COS in "External Data Management" (EDM) objects which are then linked to diagram objects, so that P&I designers can view the data.
(eBrowser) CADMATIC ActiveX component for viewing the CADMATIC 3D model in Microsoft Internet Explorer. See CADMATIC eBrowser.
Object-related data that has been created in or collected to a third-party software system can be brought to CADMATIC and saved in COS as so-called External Data Management (EDM) objects. These EDM objects can function as ready-made templates that provide the Position ID and all the necessary properties to the objects the users manage in CADMATIC P&ID and CADMATIC Plant Modeller.
EDM objects can be fully managed via the CADMATIC Web API: created, viewed, updated and deleted. This can speed up the design work considerably when the necessary objects and their attributes have already been defined, for example, in an ERP or PLM system, and the designer just needs to add the ready-made object to the P&I diagram or the 3D model. If the source database is updated, the new data can easily be pushed to CADMATIC.
EDM objects can also be imported from data stored in an open XML format such as DEXPI. Exchanging object data using the DEXPI format is especially useful in projects where different disciplines use different software tools and the data needs to be shared in an efficient way. CADMATIC supports import of objects with Position ID, and the export file can be obtained from any software that supports DEXPI XML export.
Because the imported EDM objects are stored in the COS database, in a distributed project the import can be performed at any site—the normal replication process distributes the objects to the other sites.
(eXchanger) CADMATIC ObjectARX component for converting model from AutoCAD to CADMATIC and vice versa.
Geometric Description Language
Hardwired attributes are predefined in COS. They cannot be modified in Manage COS or assigned to new object types.
Hole request object is a special Plant Modeller object which contain the information of the hole that needs to be created. See Hole Manager.
"CADMATIC Hull Classic" refers to the older version of CADMATIC Hull that did not use the COS database. The last published version was 2021T2.
Image-based lighting (IBL) is a computer graphics rendering technique that allows light to be projected on 3D objects by using an image that captures real-world lighting conditions. See User Settings.
Instructions Controlling Generation of Documents
Interactive Component Model
In Component Modeller, the parameters (such as length, width, mass, and angle) of piping components, ducting components, equipment, structural components, and beams can be defined as an instance parameter that supports a given range or set of values, which allows for fewer component models needing to be made. Then, a designer who is adding an instance of the component to the 3D model can flexibly adjust the parameter values, instead of having to locate a specific catalog part that has the exact combination of required parameter values.
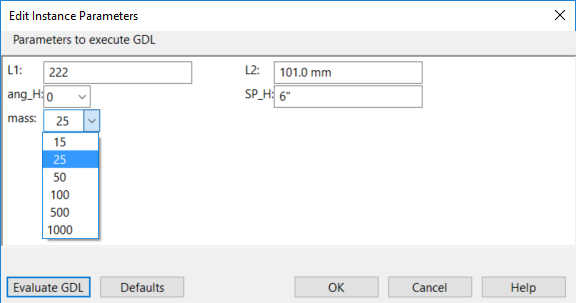
- Edit parameter definitions describes how to enable instance parameters in Component Modeller.
- Parameter values describes how to edit the instance parameters of equipment and structural components.
- Instance parameters describes how to edit instance parameters in piping.
- Instance Parameters describes how to edit instance parameters in ducting.
- Edit instance parameters describes how to edit the instance parameters of beams.
- Editing instance parameters of supports describes how to edit the instance parameters of primary supports.
In cable tray routing, if the catalog part uses angle as an instance parameter, curves will be flexibly routed along the path specified by the user, instead of being restricted to predefined angles. See Route.
[COS] The site that hosts the master project database of a given project. The main site's server can be the root server or a replica server.
[COS] The primary copy of a database.
[COS] The server from which a replica server replicates data. This data includes the database schema and possibly databases. Note that a server is a "master server" only in relation to its replica servers; a master server can be the root server of the COS network (meaning that it has no master), but it can also be a server that functions as a replica to some other master server.
Model Description Language
CADMATIC application for managing the contents of the COS server.
[COS] The site that has the master server of the local site's server. The parent site can be the main site or a satellite site.
[COS] A location such as a design office that takes part in a project. Each site has a Project Site object that the site's server owns. A single COS server can host several project databases and can thus act as the site server of many projects.
A reference drawing is a 2D drawing imported from an external DWG, DWT, DWF, DWFx, DXF, or DGN file that is attached to a work view, drawing view, or diagram, and serves as a visual aid when inserting 3D design objects, 2D diagram symbols, or 2D annotations. Reference drawings can be resized, repositioned, and customized by adjusting line weight and color, without modifying the original drawing. Reference drawings may maintain a link to the original file, or break the link during import, storing a copy of the original drawing in COS. In both cases, if modifications are made to the original, the reference drawing can be updated by reloading, and unnecessary reference drawings can be hidden or removed entirely.
[COS] A secondary copy of a database.
[COS] A server that replicates data from its master server.
[COS] A server that is not a replica server (a server that does not have a master). It hosts the primary copy of the database schema. Of the servers that use the same schema, only one can be a root server. A root server can host master databases only.
[COS] A project site that hosts a replica project database.
[COS] A schema defines the structure of a database. COS schema defines the object types and the attributes.
(P&ID) The graphical selection bar to select objects to be inserted in the diagram.
Screen space ambient occlusion (SSAO) is a computer graphics rendering technique that allows effective approximation of occlusion (diminishing) of light, such as ambient light that enters the opening of a pipe but not much further. See User Settings.
CADMATIC Plant Modeller functionality for specifying how to view a generated 3D model. See Walkaround