In CADMATIC, electrotechnical calculations mean calculating the minimum short-circuit current of groups and calculating the voltage drop in the wiring of groups. The calculations are performed automatically in association with certain functions, so the user only needs to enter the necessary basic information and to draw the drawing correctly.
Note: For calculating more complex distribution schematics, durations of short-circuit, selectivity, and, for example, for taking any motors that feed power to the network into account, any other calculation program is recommended.
Distribution board, group mark and wiring are mandatory elements needed in calculations. If you want to calculate wiring between drawings (storeys), the storey settings must also be defined. The storey settings are used to calculate the vertical displacements of wiring.
Distribution board
The distribution board acts as the starting point for calculations. With the group mark, you can tell the distribution board whether it is fed by another distribution board. Alternatively, you can add a fixed short-circuit value i.e. the minimum short-circuit current in this distribution board. The value comes from the power utility or the calculation program of the distribution network.
-
If the distribution board is fed by another distribution board in the project, a group is created in the feeding distribution board and this group is chosen as the feeder for the distribution board to be fed.
-
Short-circuit current is never calculated for incoming feeders; they either use the value of an outgoing feeder or a fixed value. If automatic calculation has been set for the incoming feeder, the value is taken from the outgoing feeder. The fixed value is used if it has been defined.
Group mark
The group mark is a link between the distribution board and wiring, and the group mark also indicates the type of cable used to feed another distribution board. The group mark has information about the wiring type in the same way as the wiring.
It is not mandatory to put a group mark in the drawing, although recommended. If a group mark can be found in the drawing, the feed length is automatically calculated from the distribution board up to the group mark, even though the group and distribution board would be located in different drawings. If a group mark has not been inserted in the drawing, the length can be entered manually for the group as a fixed value.
Wiring
Wiring drawn in the drawing extends the wiring route from the group mark to the load. Wiring shall include information about the wiring type in the same way as the group mark does. Based on the type, information about the cross-section and material is obtained for calculations. In addition, the length of wiring is calculated from the drawn wiring.
So, wiring provides information about the cross-section and material as well as the length of the drawn line. The program does not take a stand on the positioning environment of wiring and thereby on the load capability.
Wiring length / farthest point
In view of the minimum short-circuit current, it is important to know the farthest point and the distance to it. The program retrieves the farthest point in each group automatically and calculates the route length. This, however, requires that the wiring has been drawn from one wiring point to another.
The calculated wiring route consists of a route from the distribution board to the group mark, and the route along wiring to the farthest point is added to this, and any vertical displacements in wiring and symbol elevations are taken into account. The vertical displacements between storeys are also taken into account, if the distribution board is located in another drawing or the wiring route extends to another drawing. This requires, however, that the storey settings are defined, and then the storey height determines the amount of vertical displacement.
Applied formulas
The minimum short-circuit current is calculated using Thevenin's theorem. Wire impedances are calculated using specific resistances of cross-sections and material. When calculating the short-circuit current, wire resistances are corrected with a temperature factor to reflect the temperature of the wire at short-circuit. As a default, the temperature of +80 degrees Celsius is used.
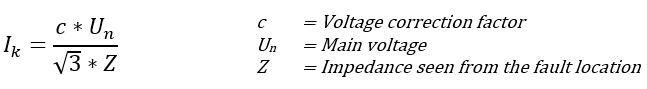
Maximum length of the cable is determined with following formula:
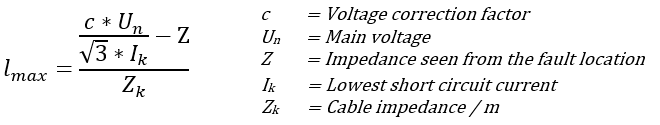
A single-phase or a three-phase voltage drop is calculated for the group. Application determines which formula is used by using information from wiring. If Wiring includes 3 or more phase wire, then is used formula to a three-phase voltage drop, otherwise is used a single-phase formula.
So far, the group does not indicate whether it is a single-phase group or a three-phase group. When the group's design current is calculated via output power, the program gives too high values for three-phased groups. This must be taken into account when reviewing the results.
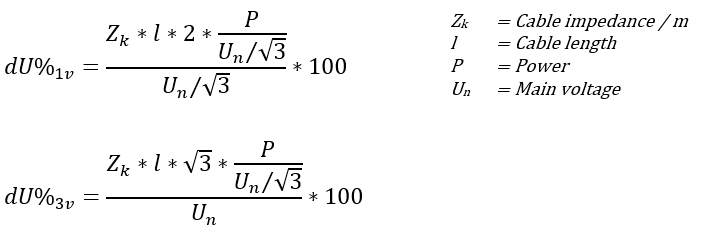
Value 1 is used as Cos phi values in all formulas.
Required short-circuit current value
The required short-circuit current value can be taken from a table or calculated using a formula, depending on the type of the protective device.
Fuse Gg (Gg fuse values can be used for a plug fuse of type D), the required values are obtained from the table using the fuse's nominal current and required switch-off time.
The required values for circuit breakers are calculated with formulas: (In = nominal current of protective device)
B = 5xIn
C = 10xIn
D = 20xIn
K = 12xIn
Z/A = 3xIn
Breakdown of results
Calculation results are shown in distribution board and feeder management, and this information is also recorded in the distribution board schematic, if there is a place provided for them in the distribution board schematic template. The data can also be exported to the clipboard. The results are illustrated for the user with color codes as follows:
|
|
The short-circuit current value is over 20% greater than required or the voltage drop is smaller than dU<2%. |
|
|
The group values cannot be calculated if a piece of information is missing. |
|
|
The short-circuit current value is 0-20% greater than the required value, or the voltage drop is in the range 2%<dU<5%. |
|
|
The short-circuit current value is below the lowest allowable value or the voltage drop is dU>5%. |
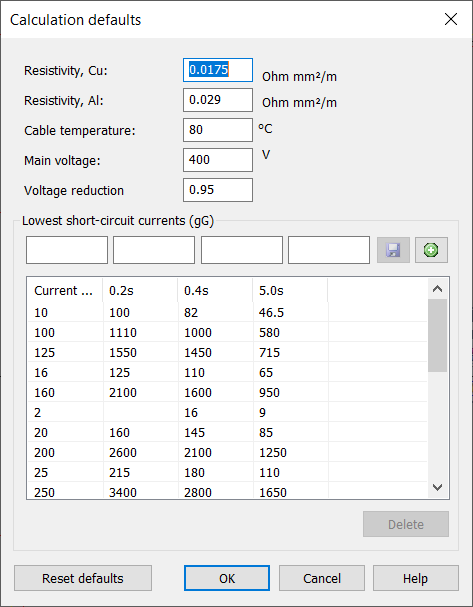
Default values used in calculation
Specific resistances and other defaults used in calculations are shown in the figure below. The Calculation defaults dialog shows the values applied to a Gg fuse; the required values for circuit-breakers are calculated according to the type of the protective device. Fuse sizes in the Current column can be selected for the circuit-breakers as well, for example in the group mark dialog box.