Drawing Views
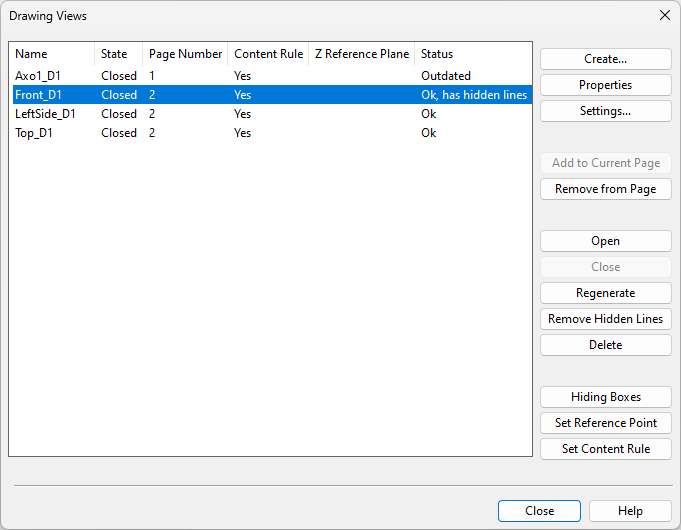
On the Home tab, in the Views group, click the Drawing Views button or select Drawing views from the button's drop-down menu to open the Drawing Views dialog where you can manage drawing views and their properties.
In the view list, hold down Ctrl or Shift to multi-select views so that you can, for example, regenerate or delete several views at the same time.
Create
The Create button opens a menu where you can select how to create a new drawing view.
Default views | Custom view | View from Point 1 to Point 2 | Copy selected drawing views | Copy views from elsewhere | Standard E-projections
Default views
Create > Default views opens the Create Default Views dialog where you can create one or more drawing views that use a predefined viewing direction.
For details, see Default Views.
Custom view
Create > Custom view opens the Create View dialog where you can enter a name for the new view to be created. For details, see Custom View.
Then, the Set Properties of View dialog opens for defining the settings of the new view. For details, see View properties.
View from Point 1 to Point 2
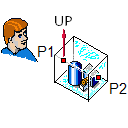
You can create a set of wireframe drawing views that show a user-defined set of objects from different angles. You can create up to five different views at the same time: a view that faces a user-defined direction, a view from top to bottom, a view from right to left, a view from left to right, and an axonometric view.
The limits of each view are defined by a bounding box that is formed by the visualized objects, the view direction, the up direction, and (optional) user-defined margin.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select Create > View from point 1 to point 2.
-
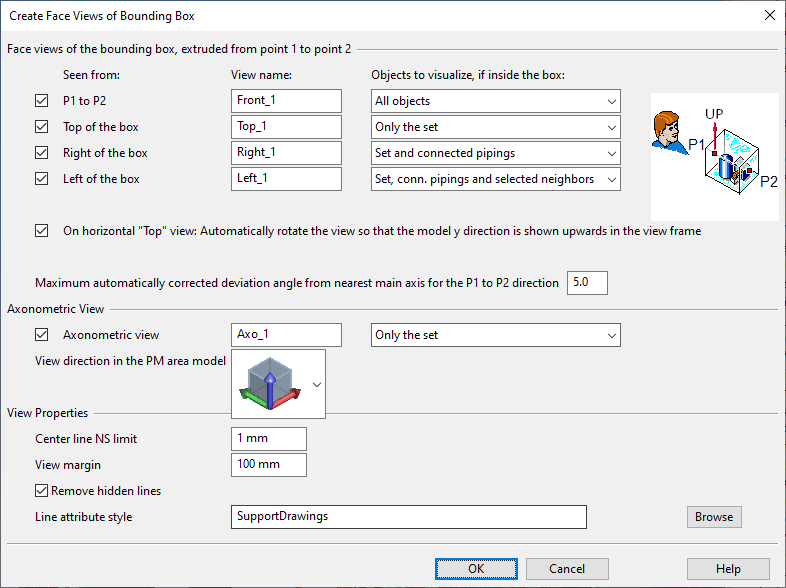
Select the objects that you want to be visualized in the view and press Enter. The Create Face Views of Bounding Box dialog opens.
-
To create a view that faces a specific direction, define the following settings:
-
Seen from – Select whether the view direction is from point 1 to point 2 or from the top, right or left side of the bounding box.
-
View name – Enter a descriptive name for the view.
-
Objects to visualize, if inside the box – Select which of the objects that are inside the bounding box to visualize in the view:
-
All objects – All objects.
-
Only the set – Objects you initially selected into the set.
-
Set and connected pipings – Objects you selected and pipes that are connected to those objects.
-
Set, conn. pipings and selected neighbors – Objects you selected, pipes that are connected to those objects, and additional objects that you will select later on during this procedure.
-
-
On horizontal "Top" view… – Select this option if you are creating a top view and you want the 3D model's Y direction to point upward in the view frame.
-
Maximum automatically corrected… – Define how many degrees the view direction can deviate from the nearest main axis direction. If the deviation is less than this value, the view is aligned with the coordinate axes of the 3D model.
-
-
To create an axonometric view, define the following settings:
-
Make sure Axonometric view is selected.
-
Enter a descriptive name for the axonometric view.
-
Select the view direction of the axonometric view from the menu.
-
Select which objects to visualize in the axonometric view.
-
-
Define the view properties:
-
Center line NS limit – Define the smallest nominal size for showing the centerline of pipes.
-
View margin – Define how many millimeters of extra space to add around the bounding box of the view.
-
Remove hidden lines – Select this option to allow hidden lines to be removed when the view is created.
-
Line attribute style – This option is shown when you are creating a drawing view. Click Browse to select a specific line attribute style for the drawing views to be created.
-
-
Click OK.
-
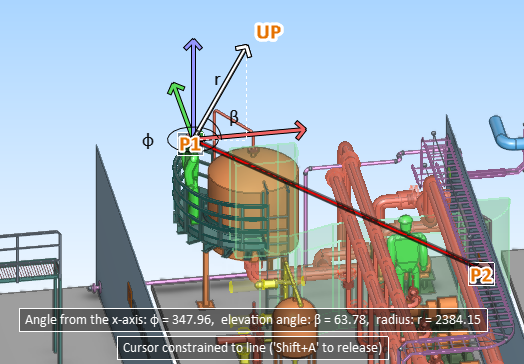
Pick a start point (P1) for the vector that defines the view direction.
-
Pick an end point (P2) for the vector that defines the view direction.
-
Define the up direction of the view. The program tries to select a suitable direction and locks the direction—press Ctrl+A if you want to release the cursor and select another direction. Click or press Space to accept the direction.
-
If you chose to include "selected neighbors" in any of the views to be created, select those additional objects and press Enter.
The specified views are created.
Copy selected drawing views
You can create one or more copies of existing drawing views.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the view or views you want to copy. Hold down Shift or Ctrl to select multiple views.
-
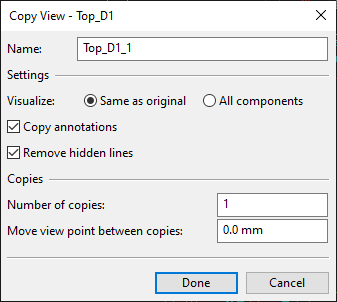
Select Create > Copy selected drawing views. The Copy View dialog opens for defining properties for the copies of the first view.
-
Fill in the following information:
-
Name – Enter a name for the new view. If creating multiple copies, the name of each additional copy will be appended with an underscore and running number.
-
Visualize – Select whether the new views should contain the same components as the original view or all components.
-
Copy annotations – Select this option to include the annotations of the original view in the new views.
-
Remove hidden lines – Select this option to remove hidden lines from the new views.
-
Number of copies – Enter the number of new views to be created.
-
Move view point between copies – You can set the viewpoint to be incrementally moved for each new view. Specify the increment in millimeters—a positive number moves the viewpoint forward, while a negative number moves it backward.
-
-
Click Done.
-
Repeat steps 3–4 for each view you selected to copy.
Copy views from elsewhere
You can copy wireframe work views or drawing views to the active document. If the work view has annotations or reference drawings, they are not copied.
Note: To be able to copy a freshly created work view you must either save the area model or close the new view first.
Do the following:
-
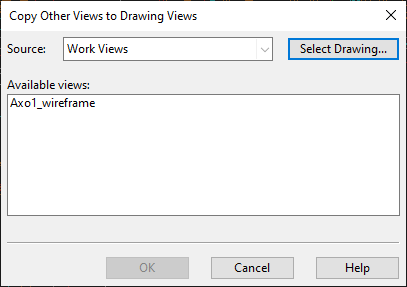
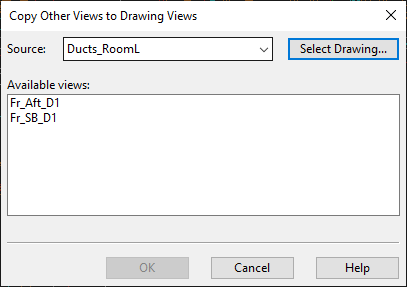
In the Drawing Views dialog, select Create > Copy views from elsewhere. The Copy Other Views to Drawing Views dialog opens.
-
Select the views to be copied:
-
To copy work views, select the work views from the list pane.
-
To copy drawing views from another document, click Select Drawing, select the document from which to copy drawing views, and then select the views from the list pane.
-
-
Click OK.
-
To stop copying views, click Cancel.
-
Use Add to Current Page to insert a copied view to the active page.
Standard E-projections
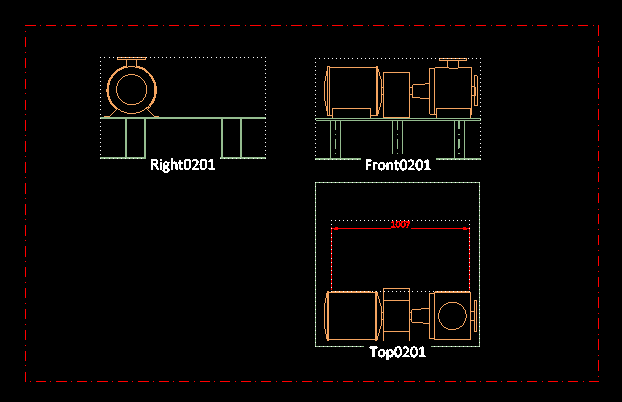
You can create standard European projections traditionally used in 3D design from selected objects. The generated views are placed on the page based on two user-defined corner points. Hidden lines are automatically removed. You can place several projection sets to one page. Also drawings with multiple pages are supported.
After the insertion, you can relocate the projection views and change their scale. You can modify these views with the normal view and visualization commands and annotate them in the same way as other drawing views.
Prerequisites
-
An open work view.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select Create > Standard E-projections.
-
You might be prompted to select which Annotation Property Defaults to use on the active page. Select the one to use and click OK.
-
Select the objects to be visualized from the active work view and press Enter. The Create Standard E-Projections dialog opens.
-
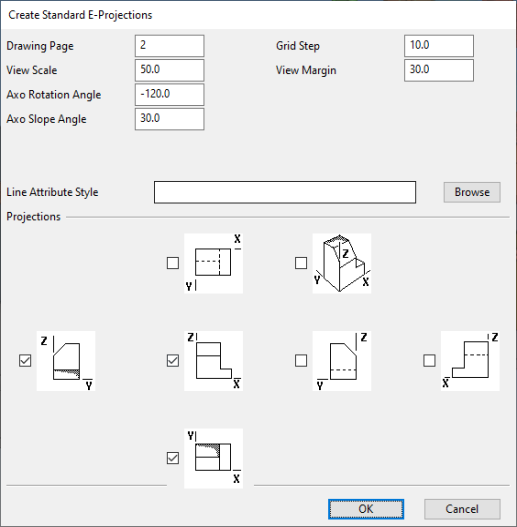
Define the settings:
 Show/hide details
Show/hide details
-
Drawing Page – Enter the number of the drawing page to which to assign the projections. The active page is the default. If you enter the number of a non-existing page, a new page will be added to the drawing and you are prompted to edit the page-specific fields and select the Annotation Property Defaults to use.
-
View Scale – Define the view scale. This scale is used in all the individual projection views to be created.
-
Axo Rotation Angle – Define the rotation angle for axonometric views. The default value is -120.
-
Axo Slope Angle – Define the slope angle for axonometric views. The default value is 30.
-
Grid Step – Define the grid step. The value must be between 1 and 100, and the default value is 10.
-
View Margin – Define the margin to include to the view limits, outside the objects to be visualized. The value must be between 1 and 1000, and the default value is 30.
-
Line Attribute Style – Select the style to use for the projections. For more information, see Select line attribute style.
-
Projections – Select the projection types to be created as separate drawing views. The drawing vies will be named in the format "ProjectionTypeXXYY" where XX is the page number and YY is the ordinal number of the projection type on that page, such as "Axo0101".
-
-
Click OK.
-
On the target page, the projection area is shown as a rectangle and you can move it to the intended location:
-
Pick the point where you want the top-left corner (origin point) of the projection area to be located.
-
Pick the point where you want the bottom-right corner of the projection area to be located.
(The size of this rectangle you draw here does not affect the scaling of the projection views inside the area.)
The projection area is drawn as a dashed rectangle and the projections are located in that area, in the same order that they were presented in the settings dialog.
-
-
You can continue creating additional standard projections or press Esc to exit the tool.
Properties
The Properties button opens the properties of the selected view for editing.
For details, see View properties.
Settings
The Settings button opens a menu with the following tools.
Rename | Select line attribute style | Change line attributes | Set color style | Set Z reference plane | Set centerline NS limit | Set scale | Set reference point
Rename
You can rename drawing views that are closed. Select the view and then Settings > Rename to open a dialog where you can enter the new name.
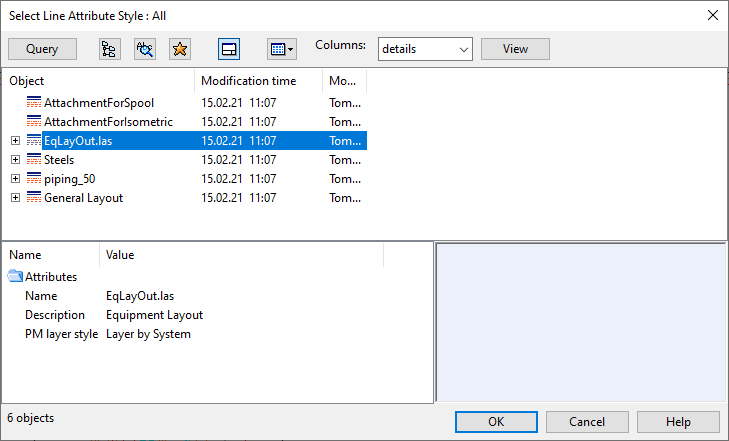
Select line attribute style
The line attribute style defines how a drawing view visualizes the edges, the hidden lines, and the centerlines of 3D objects. The line attribute style is linked to a layer style that determines to which layers the 3D objects will be assigned when the drawing is exported.
Note that the line attribute style is not applied to 2D drafting objects or annotations—their visualization is defined in tool-specific lineweight settings, as described in Annotation Properties.
Prerequisites
-
The project administrator has created the required line attribute style, as described in Line Attribute Styles.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the views where you want the setting to be applied.
-
Select Settings > Select line attribute style. The Select Line Attribute Style dialog opens.
-
Select the style from the list and click OK.
-
If you have manually set line attributes, you are prompted whether to set them to the default style.
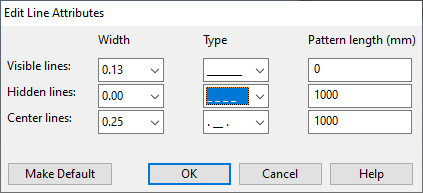
Change line attributes
You can change the line attributes of a set of objects in a drawing view.
Prerequisites
-
An open work view.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the views where you want the setting to be applied.
-
Select Settings > Change line attributes. The active work view is displayed.
-
Select the required objects and press Enter. The Edit Line Attributes dialog opens.
-
Edit the line attribute values as required and click OK.
-
Regenerate the views.
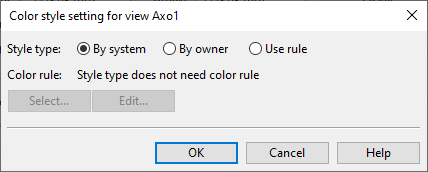
Set color style
You can set model objects in drawing views to be colored based on their System, their current owner, or surface shading rules.
Do the following:
- In the Drawing Views dialog, select the views whose color style you want to set.
-
Select Settings > Set color style. The Color style setting for view… dialog opens.
-
Select what defines the color of the model objects:
-
By system – Select this to color the objects based on the System they use. For information on defining System colors, see Creating systems.
-
By owner – Select this to color the objects based on who owns them. For more information, see Color objects by ownership.
-
Use rule – Select this to color the objects based on a Surface shading style.
-
Select – Opens a list of available surface shading styles for selecting which style to use.
-
Edit – Opens the current style for editing.
-
-
-
Click OK.
Set Z reference plane
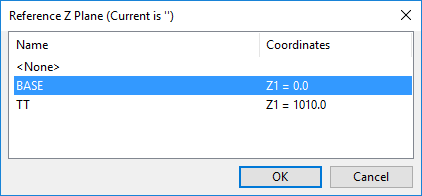
CADMATIC allows coordinates to be defined and displayed as relative to a reference plane. In drawing views, coordinate labels that show Z coordinates are normally referring to the nearest reference plane in Z direction, so the nearest plane can be, for example, either the floor or the ceiling. Set Z reference plane allows you to define the specific Z reference plane that each drawing view should use.
In the Drawing Views dialog, select one or more drawing views (hold down Ctrl or Shift to multi-select views), and then select Settings > Set Z reference plane. The Reference Z Plane dialog opens for selecting the plane to use.
After selecting the reference plane, you can open the drawing's annotation view and add coordinate labels whose coordinates are relative to a Z reference plane. Coordinates are relative to a Z reference plane when the label definition uses specific tags for data requests. Those tags are described in Attributes for label definitions using Z reference plane.
In the following example a label definition has been configured to use the data requests .Dx;-1;;.Dw;-1;;.Dv;-1;; to show distance, direction, and plane name in the third row of the coordinate label, and a label of this type has been added to the connection point of a valve. The sample image on the left shows what the label displays when the reference plane is set to "BASE" (located at 0.0 mm), while in the image on the right the reference plane is "TT" (located 1010.0 mm above "BASE").
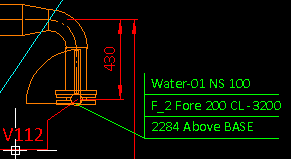
|
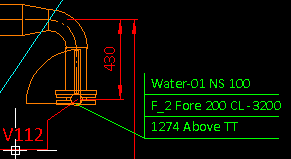
|
For information on creating and editing label definitions, see Label Definitions.
For information on creating and editing Z reference planes, see Coordinate references.
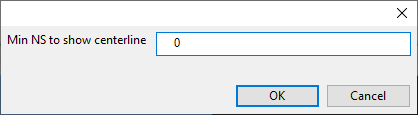
Set centerline NS limit
You can specify a minimum Nominal Size value for visualizing the pipe centerlines. If a pipe is smaller than this value specifies, then the centerline is not visualized.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the views where you want the setting to be applied.
-
Select Settings > Set centerline NS limit. A dialog opens for defining the limit.
-
Enter the required value and click OK.
-
Regenerate the views.
Set scale
You can change the scale of a drawing view. If you do this before adding any views to the page, the scale of the first view you add to the page stores the scale in the document header, in the attribute "Drawing Main Scale" (.IR) or "Drawing Detail Scale" (.IS).
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the view whose scale you want to change.
-
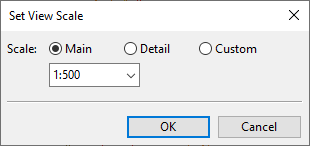
Select Settings > Set scale. The Set View Scale dialog opens.
-
Select the scale:
-
Main / Detail – Select a scale that the administrator has defined in the General Drawing settings.
-
Custom – Specify the scaling value. (This is the only possible option if main view/detail view scales are not applicable to the document type.)
-
-
Click OK.
Set reference point
You can change the reference point of a drawing view. The reference point is displayed as a cross-hair when you insert or move the drawing view on the page, and its default location is the center of the view.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the view whose reference point you want to change.
-
Select Settings > Set reference point.
-
Pick a new reference point from the 3D model.
Add to Current Page
You can select a view from the drawing view list and insert it to a suitable location on the active page. By default, the reference point is at the center of the view. You can change the reference point of a given view as described in Set reference point.
As you are placing the view on the page and moving it to the intended position, the preview image can show:
-
The bounding box around the view. You can enable or disable the displaying of the bounding box from the document settings, as described in Settings.
-
The 3D objects in the view. You can enable or disable this from the context menu of the tool, as described below.
If the first view that you add to the document has a main scale or detail scale, the scale value is stored in the attribute "Drawing Main Scale" (.IR) or "Drawing Detail Scale" (.IS), respectively. Any other view that you add later does not change the value of that attribute. Removing all views clears the attribute.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the required view from the list and then click Add to Current Page. The drawing view is displayed on the page; the cross-hair indicates where the reference point is.
-
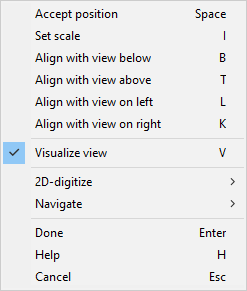
Start moving the drawing view to its intended location. If the view is large and complicated and does not move smoothly, disable the Visualize view (V) option from the context menu and see if that helps.
-
Press I or select Set scale from the context menu and use the Set View Scale dialog to specify the scale of the drawing view on the page.
-
If the page already contains another drawing view that uses the same projection and same global coordinates as the view you are adding, you can use the Align with… context-menu commands to align the views. The views are aligned based on the global axis that is parallel to the U or V axis.
-
When the view is in the intended location, press Enter or Space to accept the location and return to the Drawing Views dialog.
Remove from Page
The Remove from Page button removes the selected drawing view from the page it has been assigned to. You are prompted to confirm the action.
Removing all views from the page clears the scale value that has been stored in the document header in the attribute "Drawing Main Scale" (.IR) or "Drawing Detail Scale" (.IS).
Tip: You can also remove drawing views with the Home tab command Remove from page.
Open
The Open button opens and activates the selected views. Hold down Ctrl or Shift to select multiple views that you want to open.
Close
The Close button closes the selected views. Hold down Ctrl or Shift to select multiple views that you want to close.
Regenerate
The Regenerate button re-creates the selected views. Hold down Ctrl or Shift to select multiple views that you want to regenerate.
You should regenerate views whose current status is "Outdated" as that status indicates that the 3D model contains changes that are not visible in the view.
Regenerating restores hidden lines—use the Remove Hidden Lines tool to remove them again.
Remove Hidden Lines
In a complex three-dimensional model, it is sometimes difficult to know what objects—and which parts of those objects—are visible from a certain viewpoint and to perceive the depth of the view. The Remove Hidden Lines button removes all lines that are behind objects and thus not visible to the eye. This usually provides a more realistic image of the spatial relations of the objects in the view. Hold down Ctrl or Shift to select multiple views whose hidden lines you want to remove.
The hidden lines are restored again if you regenerate the view with the Regenerate button.
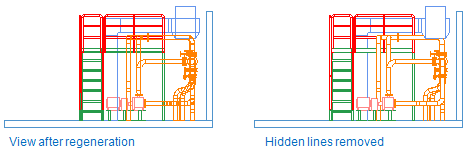
Delete
The Delete button deletes the selected views. Hold down Ctrl or Shift to select multiple views that you want to delete.
You are prompted to confirm the action.
Hiding Boxes
You can hide piping objects that are inside an adjustable box in a drawing view. You can use this when some pipes are blocking the view to some other objects that should be visible in the drawing.
Prerequisites
-
An open work view.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the target view from the list and then click Hiding Boxes.
The active work view is displayed, and any existing hiding boxes are shown in the view.
-
Use the commands in the context menu to create, edit, and delete hiding boxes.
 Show/hide details
Show/hide details
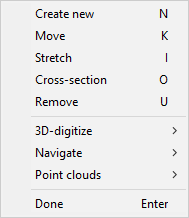
-
Create new (N) – To create a new hiding box, navigate to the start point (the center of the bottom of the box), press N, and pick the end point (the center of the top of the box).
-
Move (K) – To move a hiding box, place the cursor inside the box, press K to snap to the end point, and pick the new location of the end point.
-
Stretch (I) – To adjust the length of a hiding box, place the cursor inside the box, press I to snap to the end point, and pick the new location of the end point.
-
Cross-section (O) – To adjust the cross-section of a hiding box, place the cursor inside the box, press O to snap to the corner of the box, and pick the new location of that corner point.
-
Remove (U) – To delete a hiding box, place the cursor inside the box and press U.
-
-
Press Enter to return to the Drawing Views dialog.
For more information on hiding boxes, see Hiding boxes.
Content Rule
A content rule is a query-based filter that defines which objects are shown in a given view. The query can specify, for example, that only piping objects and equipment are shown in the view. Content rules can be created for work views and drawing views.
You can create a content rule for selected drawing views; the rule is saved in the properties of each view. To enable reuse, you can store the rule in COS or in a private file.
If you clear the view setting Filter > Show objects matching content rule, the content rule is removed from the view.
Tip: You can also manage content rules on the Drafting tab, as described in Visualization and Changes.
Create | Edit | Copy from another view | Import from COS/File | Delete
Create
You can create a content rule for one or more drawing views. If a drawing view already has a content rule, the new rule replaces the existing rule.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the drawing views to which to apply the content rule.
-
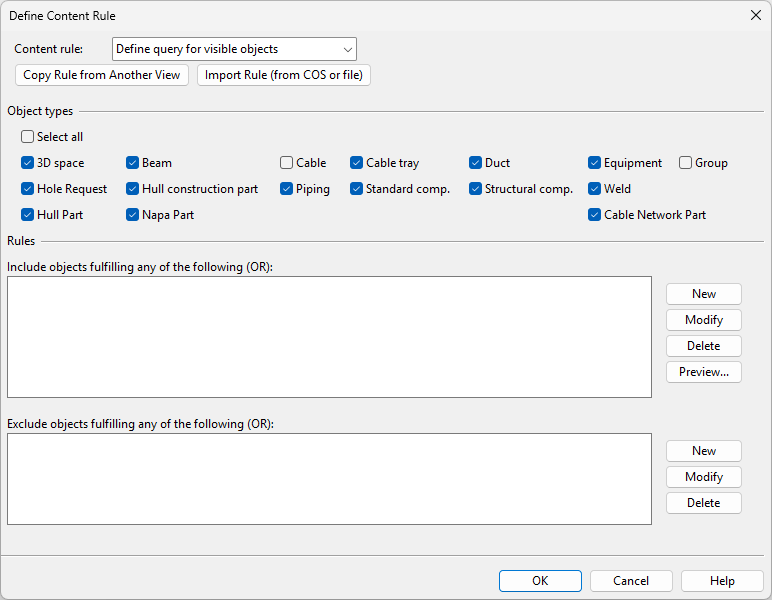
Select Content Rule > Create. The Define Content Rule dialog opens.
-
Use the query editor to define a query that selects the objects that you want to see in the views, as described in Query editor, or use the Copy Rule from Another View or Import Rule (from COS or file) functions to apply an existing query.
-
Click Save As and select where to save the query:
-
Click COS to save it as a project query that also other designers can import to any document in the same project.
-
Click File to save it as a private query that is only available to you.
-
-
Click OK to close the query editor.
Edit
You can edit the content rule of a drawing view.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the drawing view whose content rule to edit.
-
Select Content Rule > Edit. The query editor opens.
-
Edit the rule as required, and click OK.
Copy from another view
You can copy an existing content rule from another drawing view in the same document.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the drawing views to which to apply the content rule.
-
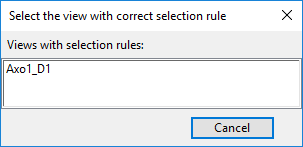
Select Content Rule > Copy from another view. The Select view with content rule dialog opens.
-
Click the name of the view from which to copy the content rule. The query editor opens, displaying the copied query.
-
Edit the query if needed, and then click OK.
Import from COS/File
You can import an existing content rule from COS or a query file.
Do the following:
- In the Drawing Views dialog, select the drawing views to which to apply the content rule.
-
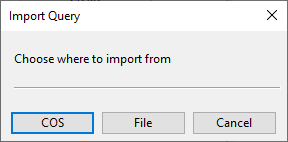
Select Content Rule > Import from COS/File. The Import Query dialog opens.
-
Select the query to be imported:
-
To import the content rule from a project query stored in COS, click COS, select the query from the object browser, and click OK.
(If there is no suitable query in COS, select Query > Advanced to create one.)
-
To import the content rule from a private query stored in a .qsr file, click File, select the file from the list, and click OK.
(If there is no suitable query file, click New to create one.)
The query editor opens, displaying the imported query.
-
- Edit the query if needed, and then click OK.
Delete
You can delete content rules from drawing views.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select one or more drawing views that have a content rule.
-
Select Content Rule > Delete.
Transparency Rule
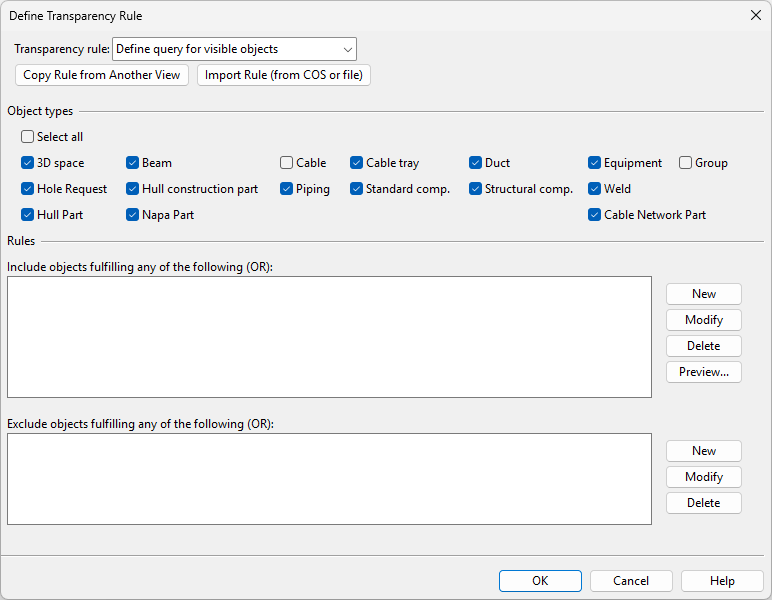
A transparency rule is a query-based filter that defines which objects are shown as transparent in a given drawing view. The query can specify, for example, that Hull objects are shown as transparent.
You can create a transparency rule for selected drawing views; the rule is saved in the properties of each view. To enable reuse, you can store the rule in COS or in a private file.
Tip: You can also manage transparency rules on the Drafting tab, as described in Visualization and Changes.
Create | Edit | Copy from another view | Import from COS/file | Delete
Create
You can create a transparency rule for one or more drawing views. If a drawing view already has a transparency rule, the new rule replaces the existing rule.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the drawing views to which to apply the transparency rule.
-
Select Transparency Rule > Create. The Define Transparency Rule dialog opens.
-
Use the query editor to define a query that selects the objects that you want to see as transparent in the views, as described in Query editor, or use the Copy Rule from Another View or Import Rule (from COS or file) functions to apply an existing query.
-
Click Save As and select where to save the query:
-
Click COS to save it as a project query that also other designers can import to any document in the same project.
-
Click File to save it as a private query that is only available to you.
-
-
Click OK to close the query editor.
Edit
You can edit the transparency rule of a drawing view.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the drawing view whose transparency rule to edit.
-
Select Transparency Rule > Edit. The query editor opens.
-
Edit the rule as required, and click OK.
Copy from another view
You can copy an existing transparency rule from another drawing view in the same document.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select the drawing views to which to apply the transparency rule.
-
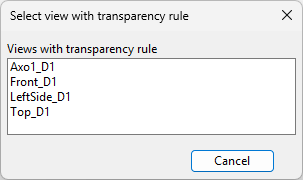
Select Transparency Rule > Copy from another view. The Select view with transparency rule dialog opens.
-
Click the name of the view from which to copy the transparency rule. The query editor opens, displaying the copied query.
-
Edit the query if needed, and then click OK.
Import from COS/file
You can import an existing transparency rule from COS or a query file.
Do the following:
- In the Drawing Views dialog, select the drawing views to which to apply the transparency rule.
-
Select Transparency Rule > Import from COS/file. The Import Query dialog opens.
-
Select the query to be imported:
-
To import the transparency rule from a project query stored in COS, click COS, select the query from the object browser, and click OK.
(If there is no suitable query in COS, select Query > Advanced to create one.)
-
To import the transparency rule from a private query stored in a .qsr file, click File, select the file from the list, and click OK.
(If there is no suitable query file, click New to create one.)
The query editor opens, displaying the imported query.
-
- Edit the query if needed, and then click OK.
Delete
You can delete transparency rules from drawing views.
Do the following:
-
In the Drawing Views dialog, select one or more drawing views that have a transparency rule.
-
Select Transparency Rule > Delete.